说明
本文档按照实验楼–Go 并发服务器框架 Zinx 入门的文档同步学习记录(大部分内容相同)
https://www.lanqiao.cn/courses/1639
主要有以下原因:
1、模仿大神写教程的风格
2、验证每一个步骤,而不是简简单单的复制教程中的代码。简单重现
实验介绍
本节实验中,我们将完成 Zinx 框架的消息封装模块。如下面的思维导图中所表示的这些功能。
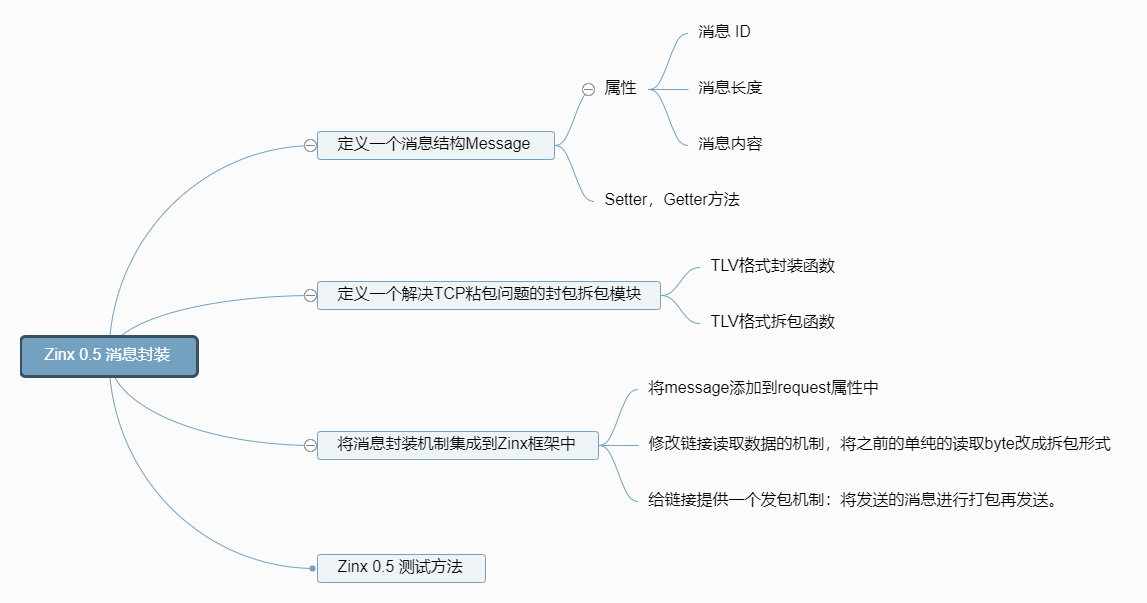
知识点
tcp 封包拆包
消息封装
Zinx 的消息封装
接下来我们再对 Zinx 做一个简单的升级,现在我们把服务器的全部数据都放在一个 Request 里,当前的 Request 结构如下:
1
2
3
4
| type Request struct {
conn ziface.IConnection
data []byte
}
|
很明显,现在是用一个[]byte来接受全部数据,又没有长度,又没有消息类型,这不科学。怎么办呢?我们现在就要自定义一种消息类型,把全部的消息都放在这种消息类型里。
创建消息封装类型
在zinx/ziface/下创建imessage.go文件: 将请求的一个消息封装到 message 中,定义抽象层接口,定义好 Getter 方法和 Setter 方法。
zinx/ziface/imessage.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| package ziface
type IMessage interface{
GetDataLen() uint32
GetMsgId() uint32
GetData() []byte
SetMsgId(uint32)
SetData([]byte)
SetDataLen(uint32)
}
|
同时创建实例 message 类,在zinx/znet/下,创建message.go文件。
整理一个基本的 message 包,会包含消息 ID,数据,数据长度三个成员,提供基本的 setter 和 getter 方法,目的是为了以后做封装优化的作用。同时也提供了一个创建一个 message 包的初始化方法NewMegPackage。
这里我们只需要要实现 Message 类,写出构造函数,实现接口中对应的方法,比较的简单,大家可以试试先自己尝试实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| package znet
type Message struct {
Id uint32
DataLen uint32
Data []byte
}
func NewMsgPackage(id uint32, data []byte) *Message {
return &Message{
Id : id,
DataLen : uint32(len(data)),
Data: data,
}
}
func (msg *Message) GeDataLen() uint32 {
return msg.DataLen
}
func (msg *Message) GetMsgId() uint32 {
return msg.Id
}
func (msg *Message) GetData() []byte {
return msg.Data
}
func (msg *Message) SetDataLen(len uint32) {
msg.DataLen = len
}
func (msg *Message) SetMsgId(msgId uint32) {
msg.Id = msgId
}
func (msg *Message) SetData(data []byte){
msg.Data = data
}
|
消息的封包与拆包
我们这里就是采用经典的 TLV(Type-Len-Value)封包格式来解决 TCP 粘包问题吧。
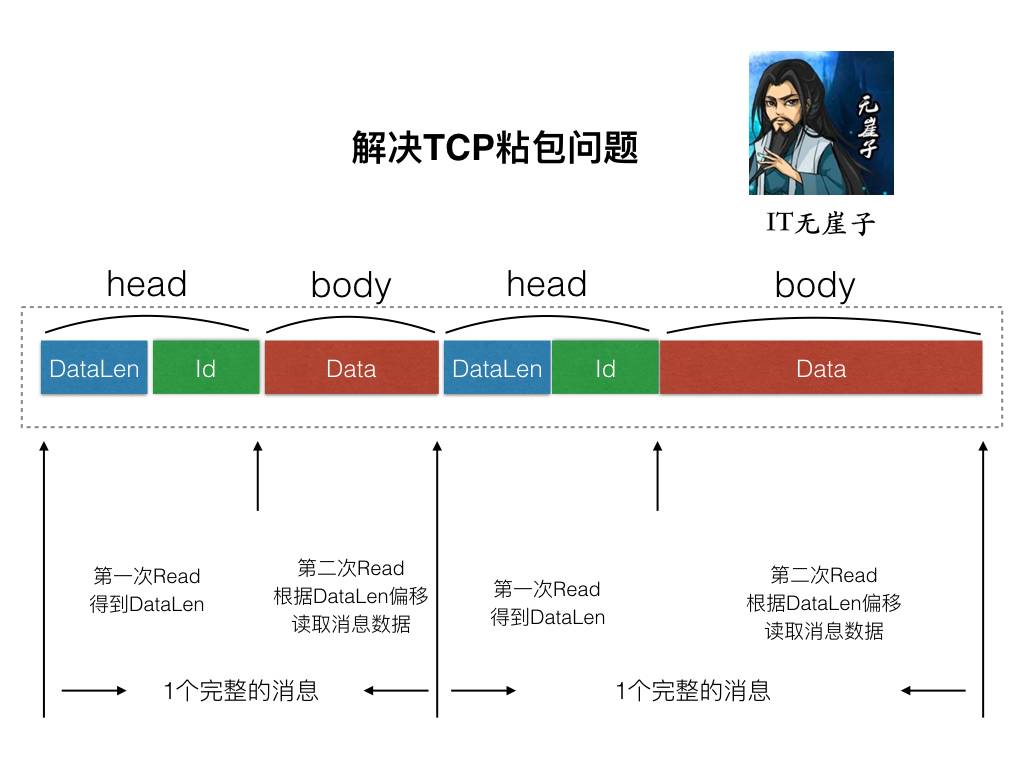
图片来源于 zinx 作者。
由于 Zinx 也是 TCP 流的形式传播数据,难免会出现消息 1 和消息 2 一同发送,那么 zinx 就需要有能力区分两个消息的边界,所以 Zinx 此时应该提供一个统一的拆包和封包的方法。在发包之前打包成如上图这种格式的有 head 和 body 的两部分的包,在收到数据的时候分两次进行读取,先读取固定长度的 head 部分,得到后续 Data 的长度,再根据 DataLen 读取之后的 body。这样就能够解决粘包的问题了。
创建拆包封包抽象类
在zinx/ziface下,创建idatapack.go文件
我们需要三个方法:
封包数据。
拆包数据。
得到头部长度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| package ziface
type IDataPack interface {
GetHeadLen() uint32
Pack(msg IMessage)([]byte,error)
Unpack([]byte)(IMessage,error)
}
|
实现拆包封包类
在zinx/znet/下,创建datapack.go文件.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| package znet
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/binary"
"errors"
"zinx/ziface"
"zinx/utils"
)
type DataPack struct {}
func NewDataPack() *DataPack {
return &DataPack{}
}
func (dp *DataPack) GetHeadLen() uint32 {
return 8
}
func (dp *DataPack) Pack(msg ziface.IMessage) ([]byte, error) {
dataBuff := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte{})
if err := binary.Write(dataBuff,binary.LittleEndian,msg.GetDataLen()); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := binary.Write(dataBuff,binary.LittleEndian,msg.GetMsgId()); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := binary.Write(dataBuff,binary.LittleEndian,msg.GetData()); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return dataBuff.Bytes(), nil
}
func (dp *DataPack) Unpack(binaryData []byte ) (ziface.IMessage ,error){
dataBuff := bytes.NewReader(binaryData)
msg := &Message{}
if err := binary.Read(dataBuff, binary.LittleEndian, &msg.DataLen); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := binary.Read(dataBuff, binary.LittleEndian,&msg.Id); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if (utils.GlobalObject.MaxPacketSize > 0 && msg.DataLen > utils.GlobalObject.MaxPacketSize){
return nil,errors.New("Too Large msg data recieved")
}
return msg, nil
}
|
需要注意的是整理的Unpack方法,因为我们从上图可以知道,我们进行拆包的时候是分两次过程的,第二次是依赖第一次的 dataLen 结果,所以Unpack只能解压出包头 head 的内容,得到 msgId 和 dataLen。之后调用者再根据 dataLen 继续从 io 流中读取 body 中的数据。
测试拆包封包功能
为了容易理解,我们先不用集成 zinx 框架来测试,而是使用 Server 和 Client 来测试一下封包拆包的功能。
TestPackServer.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net"
"zinx/znet"
)
func main() {
listenner,err := net.Listen("tcp","127.0.0.1:7777")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("server listen err:",err)
return
}
for {
conn, err := listenner.Accept()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(" server accept error", err)
}
go func(conn net.Conn) {
dp := znet.NewDataPack()
for {
headData := make([]byte,dp.GetHeadLen())
_,err := io.ReadFull(conn, headData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(" read head error",err)
}
msgHead,err := dp.Unpack(headData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(" server unpack error",err)
}
if msgHead.GetDataLen() > 0 {
msg := msgHead.(*znet.Message)
msg.Data = make([]byte, msg.GetDataLen())
_,err := io.ReadFull(conn, msg.Data)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(" server unpack data err:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println(" ==> Recv Msg : ID=",msg.Id,",len=",msg.DataLen,",data=",string(msg.Data))
}
}
}(conn)
}
}
|
TestPackClient.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"zinx/znet"
)
func main() {
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", "127.0.0.1:7777")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("client dial err:", err)
return
}
dp := znet.NewDataPack()
msg1 := &znet.Message{
Id: 0,
DataLen:5,
Data: []byte{'h','e','l','l','o'},
}
sendData1, err := dp.Pack(msg1)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(" client pack msg1 err", err)
return
}
msg2 := &znet.Message{
Id:1,
DataLen:7,
Data: []byte{'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!', '!'},
}
sendData2 , err := dp.Pack(msg2)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(" client pack msg2 err:", err)
return
}
sendData1 = append(sendData1,sendData2...)
conn.Write(sendData1)
select {
}
}
|
这里,我们的消息封装模块就完成了,下面我们将其集成到 zinx 中。
Zinx-V0.5 代码实现
Request 字段修改
首先我们要将我们之前的 Request 中的[]byte类型的 data 字段改成 Message 类型.。并且我们需要把 irequest 的方法新增一个 GetMsgID。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package znet
import "zinx/ziface"
type Request struct {
conn ziface.IConnection
msg ziface.IMessage
}
func(r *Request) GetConnection() ziface.IConnection {
return r.conn
}
func(r *Request) GetData() []byte {
return r.msg.GetData()
}
func (r *Request) GetMsgID() uint32 {
return r.msg.GetMsgId()
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| package ziface
type IRequest interface{
GetConnection() IConnection
GetData() []byte
GetMsgID() uint32
}
|
集成拆包过程
接下来我们需要在 Connection 的StartReader()方法中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| func (c *Connection) StartReader() {
fmt.Println("Reader Goroutine is running")
defer fmt.Println(c.RemoteAddr().String(), " conn reader exit!")
defer c.Stop()
for {
dp := NewDataPack()
headData := make([]byte, dp.GetHeadLen())
if _, err := io.ReadFull(c.GetTCPConnection(), headData); err != nil {
fmt.Println("read msg head error ", err)
c.ExitBuffChan <- true
continue
}
msg , err := dp.Unpack(headData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("unpack error ", err)
c.ExitBuffChan <- true
continue
}
var data []byte
if msg.GetDataLen() > 0 {
data = make([]byte, msg.GetDataLen())
if _, err := io.ReadFull(c.GetTCPConnection(), data); err != nil {
fmt.Println("read msg data error ", err)
c.ExitBuffChan <- true
continue
}
}
msg.SetData(data)
req := Request{
conn:c,
msg:msg,
}
go func (request ziface.IRequest) {
c.Router.PreHandle(request)
c.Router.Handle(request)
c.Router.PostHandle(request)
}(&req)
}
}
|
提供封包方法
现在我们已经将拆包的功能集成到 Zinx 中了,但是使用 Zinx 的时候,如果我们希望给用户返回一个 TLV 格式的数据,总不能每次都经过这么繁琐的过程,所以我们应该给 Zinx 提供一个封包的接口,供 Zinx 发包使用。 我们在 iconnection.go 中新增 SendMsg()方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package ziface
import "net"
type IConnection interface {
Start()
Stop()
GetTCPConnection() *net.TCPConn
GetConnID() uint32
RemoteAddr() net.Addr
SendMsg(msgId uint32, data []byte) error
}
|
然后,我们到 connection.go 中实现这个方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func (c *Connection) SendMsg(msgId uint32, data []byte) error {
if c.isClosed == true {
return errors.New("Connection closed when send msg")
}
dp := NewDataPack()
msg, err := dp.Pack(NewMsgPackage(msgId, data))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Pack error msg id = ", msgId)
return errors.New("Pack error msg ")
}
if _, err := c.Conn.Write(msg); err != nil {
fmt.Println("Write msg id ", msgId, " error ")
c.ExitBuffChan <- true
return errors.New("conn Write error")
}
return nil
}
|
注意,做出修改后,我们需要在 connection.go 中将 io 和 errors 包引入进来。
现在我们所需要的方法就全部完成了,下面我们来编写功能测试模块。
使用 Zinx-V0.5 完成应用程序
我们这里测试依然继续使用 Server.go 和 Client.go 的方法。
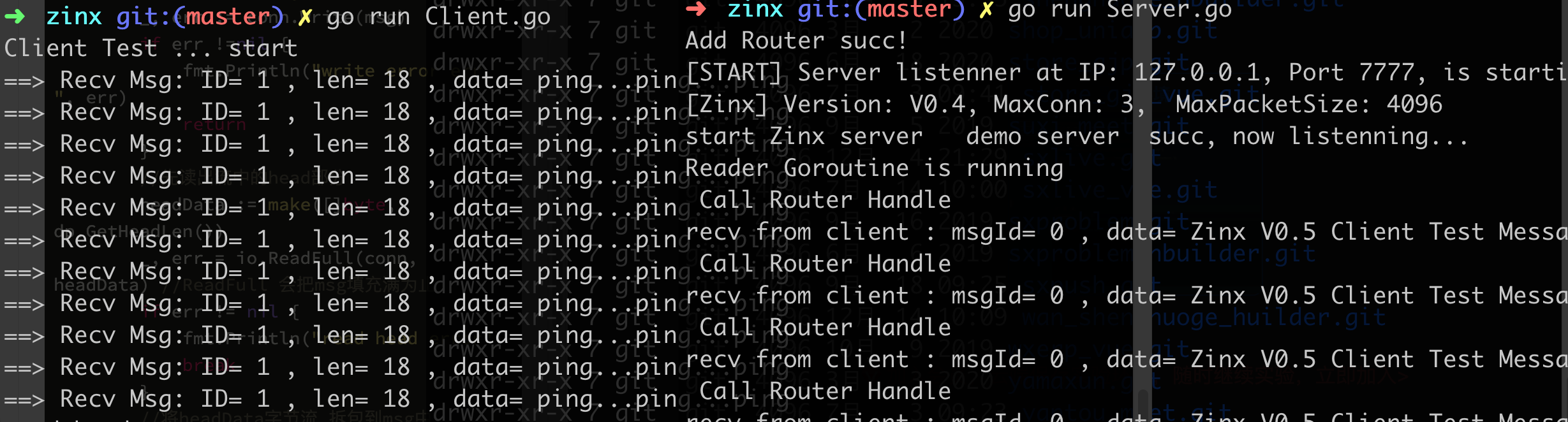
当前 Server 端是先把客户端发送来 Msg 解析,然后返回一个 MsgId 为 1 的消息,消息内容是”ping…ping…ping”
Server.go:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"zinx/znet"
"zinx/ziface"
)
type PingRouter struct {
znet.BaseRouter
}
func (this *PingRouter) Handle(request ziface.IRequest){
fmt.Println(" Call Router Handle")
fmt.Println("recv from client : msgId=", request.GetMsgId(), ", data=", string(request.GetData()))
err := request.GetConnection().SendMsg(1, []byte("ping...ping...ping"))
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("call back ping err")
}
}
func main() {
s := znet.NewServer()
s.AddRouter(&PingRouter{})
s.Serve()
}
|
这里 Client 客户端,模拟一个 MsgId 为 0 的”Zinx V0.5 Client Test Message”消息,然后把服务端返回的数据打印出来。
Client.go:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| package main
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"time"
"io"
"zinx/znet"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Client Test ... start")
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
conn,err := net.Dial("tcp", "127.0.0.1:7777")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("client start err, exit!")
return
}
for {
dp := znet.NewDataPack()
msg, _ := dp.Pack(znet.NewMsgPackage(0,[]byte("Zinx V0.5 Client Test Message")))
_, err := conn.Write(msg)
if err !=nil {
fmt.Println("write error err ", err)
return
}
headData := make([]byte, dp.GetHeadLen())
_, err = io.ReadFull(conn, headData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("read head error")
break
}
msgHead, err := dp.Unpack(headData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("server unpack err:", err)
return
}
if msgHead.GetDataLen() > 0 {
msg := msgHead.(*znet.Message)
msg.Data = make([]byte, msg.GetDataLen())
_, err := io.ReadFull(conn, msg.Data)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("server unpack data err:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("==> Recv Msg: ID=", msg.Id, ", len=", msg.DataLen, ", data=", string(msg.Data))
}
time.Sleep(1*time.Second)
}
}
|
测试结果: